Identifying a confused cell identity for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
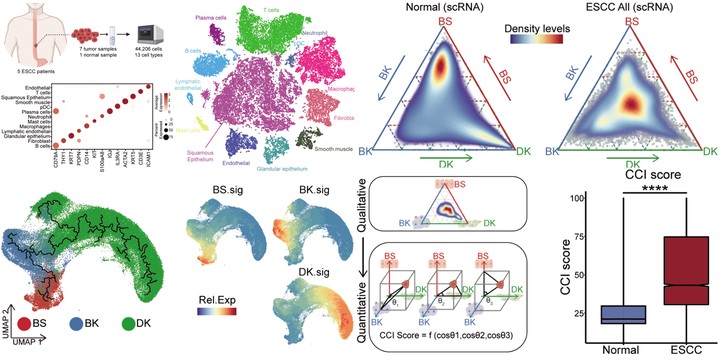
The cell identity of malignant cells and how they acquire it are fundamental for our understanding of cancer. Here, we report that esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells display molecular features equally similar but distinct to all three types of normal esophageal epithelial cells, which we term as confused cell identity (CCI). CCI is an independent prognostic marker associated with poor prognosis in ESCC. Further, we identify tropomyosin 4 (TPM4) as a critical CCI gene that promotes the aggressiveness of ESCC in vitro and in vivo. And TPM4 creates CCI through activating the Jak/STAT-SOX2 pathway. Thus, our study suggests an unrecognized feature of ESCC cells, which might be of value for clinic prognosis and potential interference.
Data availability The array data of transcriptome were downloaded by GEOquery, including GSE20347,56 17 paired normal and ESCC samples; GSE23400_1,57 53 paired normal and ESCC samples; GSE23400_2,58 51 paired normal and ESCC samples; GSE70409,59 17 paired normal and ESCC samples; GSE53624,36 119 paired normal and ESCC samples. The probe id in GSE53624 had been converted to gene name by GPL18109 platform, and others had done by feature data of getGEO results. The TPM data of bulk RNA-seq and the data of proteomics from GSE14960937 had been used in this study. In TCGA-ESCA cohorts, the 81 ESCC patients were extracted to analyze. Besides, the transcriptome data, survival information, and clinical classification of ESCC patients, from TCGA-ESCC and GSE53624 cohorts, were used to validate the clinical correlation between CCI and ESCC diagnosis. The Cox regression and the Kaplan-Meier survival curves were calculated and visualized by R package, survminer and survival. The determination of the cut-points for numerical variables in survival plots was based on the maxstat package, which also was integrated into the survminer package. The single-cell data of normal esophageal tissue was downloaded from HCA projects and the human cell landscape. And squamous epitheliums were extracted following the origin annotation. After the same scRNA data pipeline analysis, the HCA and our normal sample were combined to reduce the dimension, and the UMAP map of normal esophageal squamous epitheliums was generated, and the expression levels of classical genes and gene-sets were projected and summarized. The single-cell data of ESCC were downloaded from GSE160269. The squamous epitheliums were identified following the origin annotation. The clinical information of ESCC patients was used to divide patients into two groups including stage I and stage II/III. The raw data of RNA-seq and scRNA-seq data in this study are deposited in NCBI GEO (GSE188955). Code availability The analysis code can be found at GitHub.