KMT2C deficiency promotes small cell lung cancer metastasis through DNMT3A-mediated epigenetic reprogramming
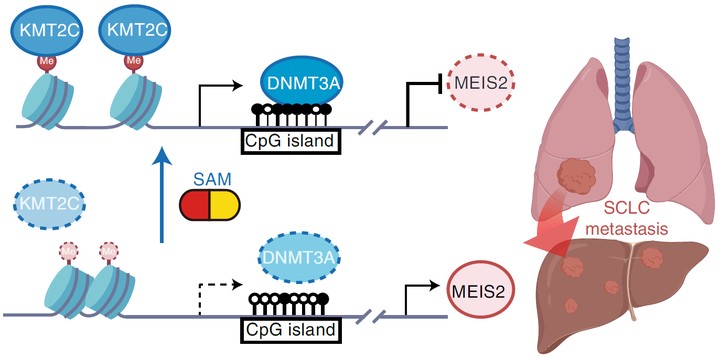 Image credit:
Unsplash
Image credit:
Unsplash
Abstract
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is notorious for its early and frequent metastases, which contribute to it as a recalcitrant malignancy. To understand the molecular mechanisms underlying SCLC metastasis, we generated SCLC mouse models with orthotopically transplanted genome-edited lung organoids and performed multiomics analyses. We found that a deficiency of KMT2C, a histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferase frequently mutated in extensive-stage SCLC, promoted multiple-organ metastases in mice. Metastatic and KMT2C-deficient SCLC displayed both histone and DNA hypomethylation. Mechanistically, KMT2C directly regulated the expression of DNMT3A, a de novo DNA methyltransferase, through histone methylation. Forced DNMT3A expression restrained metastasis of KMT2C-deficient SCLC through repressing metastasis-promoting MEIS/HOX genes. Further, S-(5′-adenosyl)-l-methionine, the common cofactor of histone and DNA methyltransferases, inhibited SCLC metastasis. Thus, our study revealed a concerted epigenetic reprogramming of KMT2C- and DNMT3A-mediated histone and DNA hypomethylation underlying SCLC metastasis, which suggested a potential epigenetic therapeutic vulnerability.
Data availability The RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, CUT&Tag, WGBS and scRNA-seq data in this study are deposited in the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus under accession number GSE161570. The processed files for omics analysis were submitted to the Figshare database. The SCLC genomics data were downloaded from cBioPortal. The omics data of 39 SCLC cell lines were accessed from the CCLE database of the depmap portal, including the mutation, CpG methylation, RNA-seq and annotation information. The RNA-seq data and clinical data of 81 individuals with SCLC were downloaded from ref. 21. The RNA-seq data of 86 individuals with SCLC were downloaded from ref. 47. The RNA-seq data of 120 SCLC CDX samples were downloaded from ref. 48. The scRNA-seq data of individuals with SCLC were downloaded from ref. 20. Source data are provided with this paper. All other data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability The analysis code can be found at GitHub.